

Tea and coffee have since served as the major beverage sources of caffeine but in the late 1800’s caffeinated soda entered the marketplace in the branded products, Dr. In the 17th century, once shipped from overseas the consumption of coffee in Europe became more common and consequently spread to the colonies in North America. By the 14th century the roasting of coffee beans had been discovered and by the 15th and 16th centuries, knowledge of its stimulating effect had apparently led to widespread consumption and commercialization in coffee houses in Arabia and Constantinople. However, caffeine would not be isolated as the active constituent of coffee’s stimulating effects until 1819 followed by its first total synthesis in 1895. In reality the first use of coffee infusions with boiling water appears around 1000 CE. Consequently, the shepherd began consuming them and experienced what is now in modern times recognized as the central nervous system (CNS) stimulation from caffeine in the berries. Ĭoffee’s introduction is similarly linked with mythology and ambiguity with legend indicating the first apparent consumption in either Ethiopia or the southern tip of the Arabian Peninsula in the 9th century by a shepherd who deduced that the wild coffee berries his goats consumed, were responsible for their display of increased energy. Prior to this recent discovery the first confirmed historical consumption of tea was 750 CE. Although this account may in fact be mythological, recent evidence demonstrates tea consumption in China as far back as 2,100 years ago during the Western Han Dynasty which ruled from 207 BCE to 9 BCE.
It has been consumed for thousands of years by humans with stories indicating the earliest consumption of boiled tea in China in the year 2737 BCE by the emperor Shen Nung, supposedly after tea leaves fell or blew into his boiling water. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.1. Introduction with a brief history of caffeine consumptionĬaffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) is a psychostimulant purine-like alkaloid, which is found naturally in coffee, tea, cacao beans (source for chocolate and cocoa) guarana, mate, and kola nuts, though it has been identified in more than 60 plant species. Bananas as an energy source during exercise: a metabolomics approach.
#Caffeine structure 3d transparent update#
The DAWN report: update on emergency department visits involving energy drinks: a continuing public health concern.
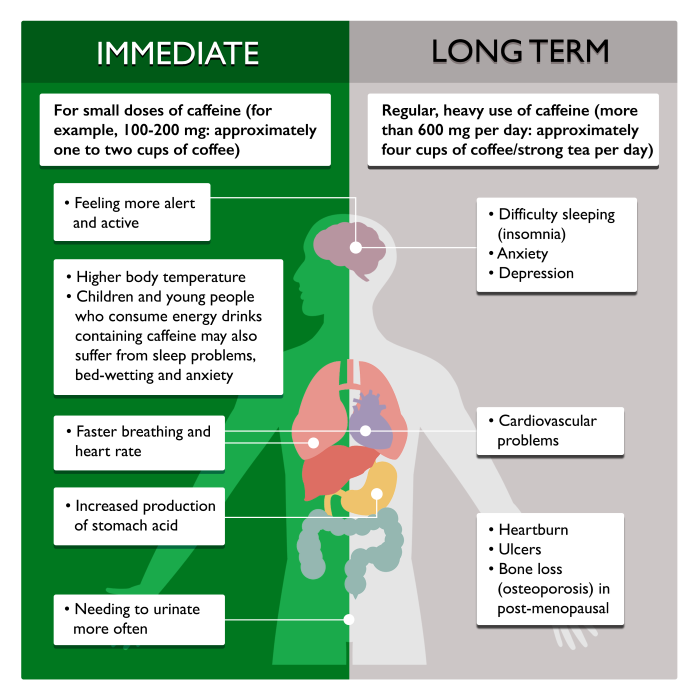
The impact of genetic variations in adora2a in the association between caffeine consumption and sleep. Dangerous mistake: an accidental caffeine overdose. Caffeine-related deaths: manner of deaths and categories at risk. doi:10.1177/0960327113510536Ĭappelletti S, Piacentino D, Fineschi V, Frati P, Cipolloni L, Aromatario M. Rhabdomyolysis induced by excessive coffee drinking. The clinical toxicology of caffeine: a review and case study. Guidance for industry: highly concentrated caffeine in dietary supplements. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism. Acute ingestion of caffeinated chewing gum improves repeated sprint performance of team sport athletes with low habitual caffeine consumption. Caffeine.Įvans M, Tierney P, Gray N, Hawe G, Macken M, Egan B. Moderate daily caffeine intake during pregnancy may lead to smaller birth size. What is the relationship between high-dose caffeine consumption and health?.Īmerican Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. The safety of ingested caffeine: a comprehensive review. Temple JL, Bernard C, Lipshultz SE, Czachor JD, Westphal JA, Mestre MA. Caffeine consumption through coffee: content in the beverage, metabolism, health benefits and risks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
